
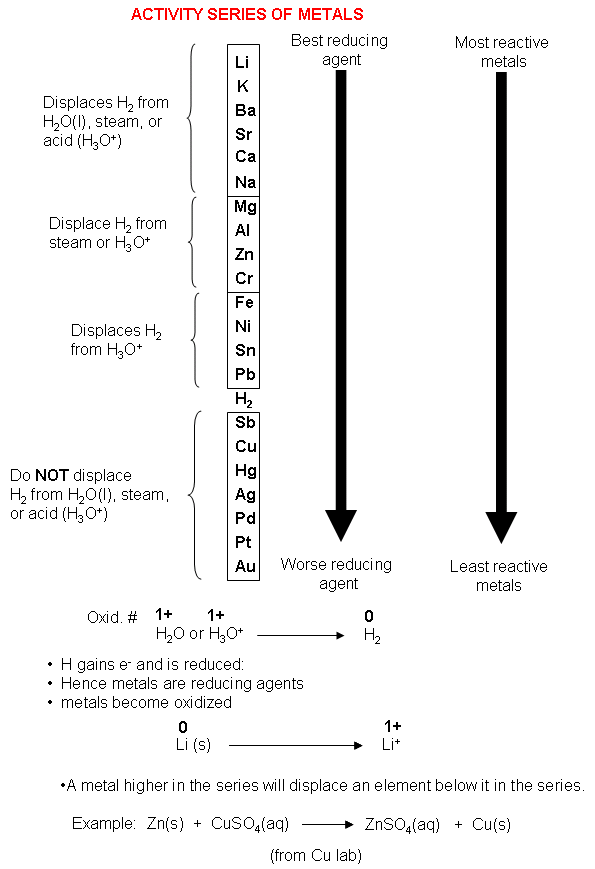

For example, calcium is quite reactive with water, whereas magnesium does not react with cold water but does displace hydrogen from steam. The boundary between the metals that react with water and those that don't is harder to spot. Those metals that can displace H + ions from acids are easily recognized by their position above H in the activity series.
Chemical activity series series#
The series begins with lithium, potassium, calcium. Less active metals like iron or zinc cannot displace hydrogen from water but do readily react with acids: The metal activity series indicates the reactivity of metals and how strongly they are reduced. Sodium is highly active and is able to displace hydrogen from water: It is important to distinguish between the displacement of hydrogen from an acid and hydrogen from water. However, silver cannot displace copper ions from solution. * Some caveats: for example, aluminium will react slowly with water, if the thin aluminium oxide layer that prevents it from reacting is damaged.(aq) + Cu(s)\] * This graphic doesn’t contain every metal in the periodic table. Majority of metals occur naturally in compounds, which we must remove them from. Some metals are so unreactive they occur largely uncombined with other elements, simple to obtain. For example, magnesium metal can displace hydrogen ions from solution. This is because they can react with the compounds in metal ores, and displace the metals, aiding with their extraction. An activity series is a list of substances ranked in order of relative reactivity. Carbon and hydrogen are also shoehorned in between entries in the list, despite being non-metals. Copper sulfate + zinc → zinc sulfate + copper Magnesium sulfate + zinc → NO REACTION The reactivity series also gives us an insight into why different metals are extracted from their ores in different ways. In order of decreasing reactivity, the metals potassium, sodium, lithium, calcium, magnesium, zinc, iron and copper can be put in order of their reactivity from. Conversely, if we react a metal with another metal lower in the series, no reaction will take place. The more reactive metal will take the place of the less reactive metal in the compound. Etymology and history Eduard Buchner By the late 17th and early 18th centuries, the digestion of meat by stomach secretions and the conversion of starch to sugars by plant extracts and saliva were known but the mechanisms by which these occurred had not been identified.

If a metal compound reacts with a metal that’s above it in the reactivity series, a displacement reaction will occur. Uses of this: * predict the outcome of certain chemical reactions.

Transition metals are much less reactive Gold and platinum have little in the way of chemical reaction. Closely followed by the marginally less reactive group 2 metals. Sometimes, it is called an activity series, especially if you are. Metals have a range of reactivities: Videos: the classic alkali metals in water demonstration The reactivity series offers a ranking of the metals in order of their reactivity. Chemical activity series (C.A.S.) is the arrangement of metals in a descending order according to the degree of their chemical activity. The reactivity series is a list of metals ordered from most reactive to least reactive. The text below has been excerpted from Compound Chemistry Student handout: Reactivity Series of Metals (PDF) This graphic places a selection of common metals into order of reactivity, as well as showing their reactions with air, water and steam.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
